Variable fonts are a highly customizable font technology. The Adobe Fonts variable font panel allows you to adjust the appearance of variable fonts and choose the best style to suit your projects. Creative Cloud apps that currently support variable fonts are Photoshop, InDesign, and Illustrator.
What are variable fonts?
Variable fonts use one file to store many font styles, as opposed to static fonts which use separate files for every style available. They allow you to specify a value for each design axis of a font, giving you control over the font’s appearance that static fonts are not capable of.
Traditional static fonts require you to add or install each individual style that you would like to use in your project. For example, with Acumin Pro, you might add Acumin Pro Regular, Acumin Pro Italic, and any other styles you want access to. Acumin Variable contains all styles of Acumin, so you would only need to add one font.


Each configuration of a variable font is called an instance. Instances are preset styles created for quick access. The variable font panel pictured above shows that Acumin Variable is set to a default instance — a predetermined setting all variable fonts fall back on prior to customization.
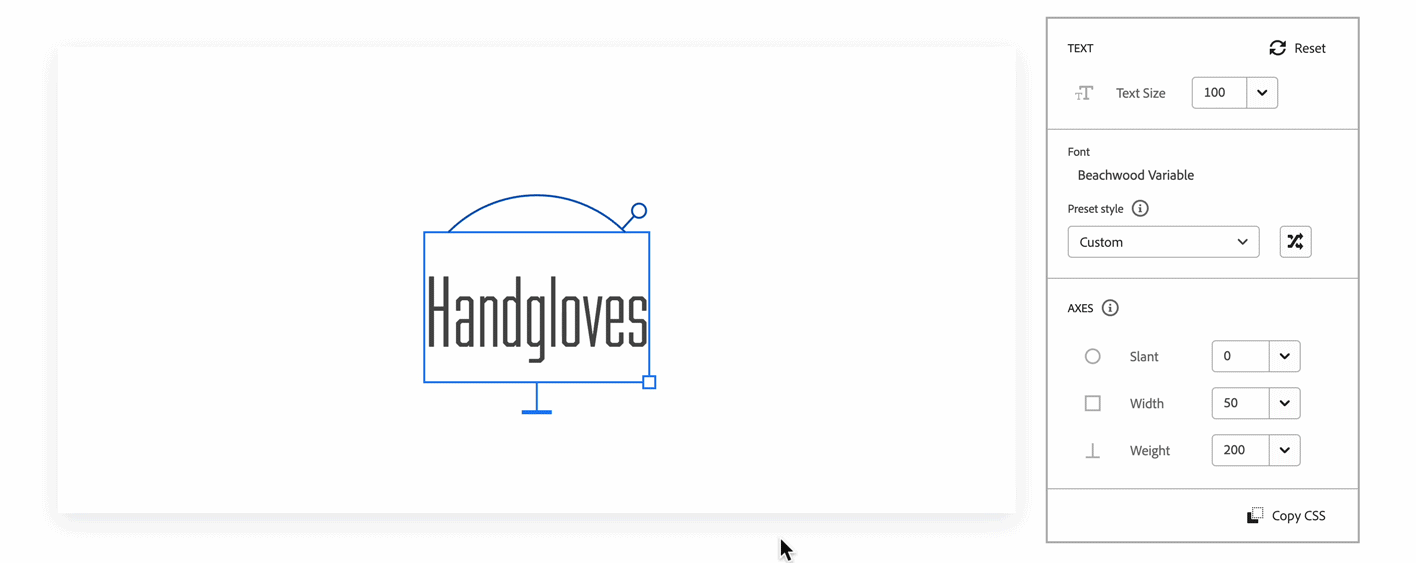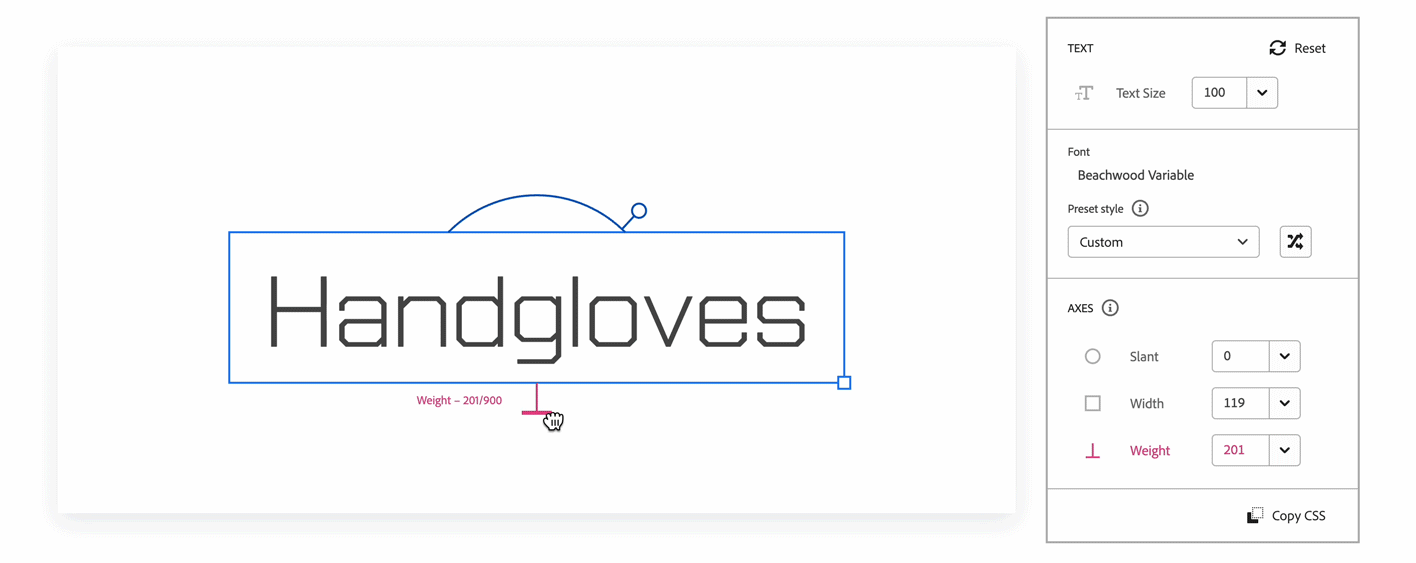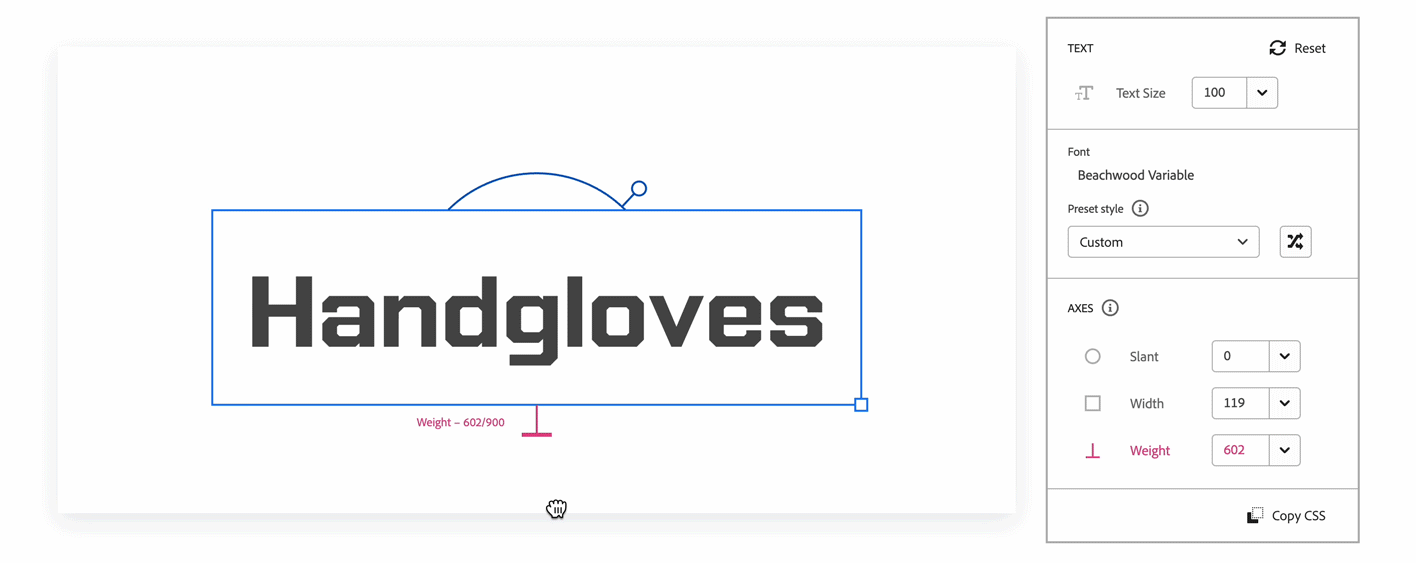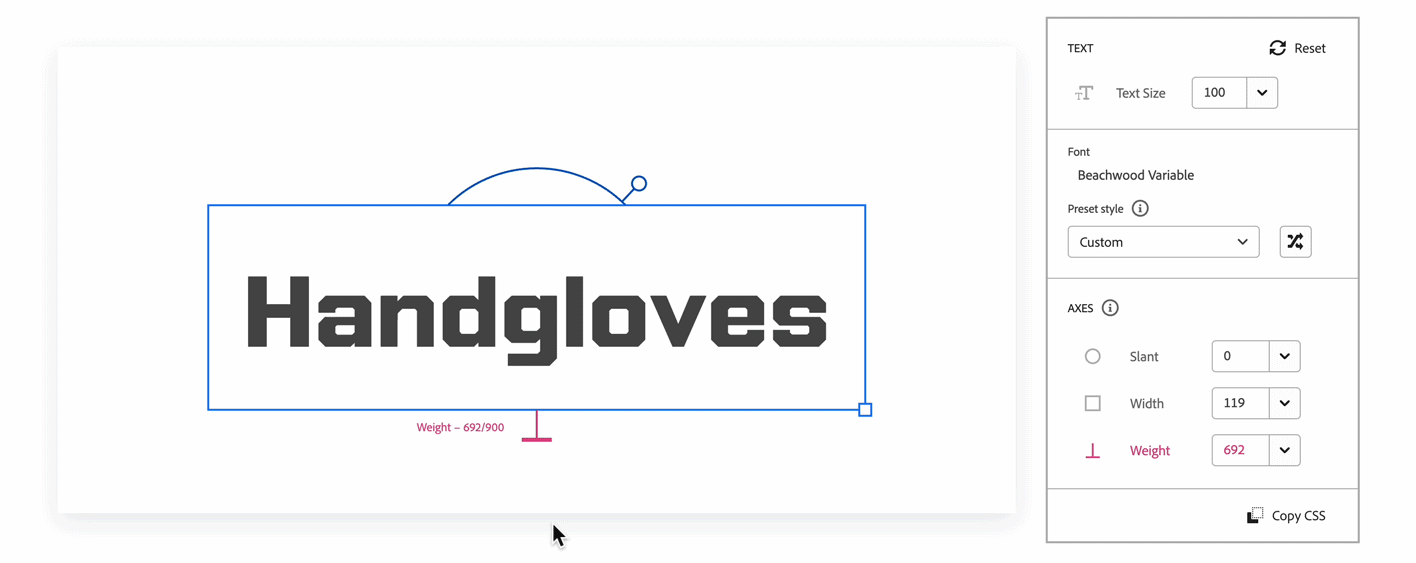
Further down the panel are the axis controls. Axes represent a continuous range of style variations. One variable font can contain multiple axes. You can customize an axis to any number within its minimum or maximum range. In the example of the Acumin Variable, the axes are Slant, Weight, and Width.
How to use variable fonts on the Adobe Fonts website
Every family detail page for variable fonts on the Adobe Fonts website includes an interactive text tool and panel that allows you to customize the font to your desired style. You can choose a preset instance to quickly manipulate or create your own.

Add a variable font to a web project
To save a variable font in your web project, select add to web project above the variable font panel on the family page. Ensure the correct font is selected; some variable fonts have additional fonts within their family.


Select Copy CSS at the bottom of the panel to grab the code corresponding to the custom instance you create. The code will reflect a default instance if there are no custom settings.
?$png$&jpegSize=100&wid=300)
?$png$&jpegSize=100&wid=300)
You can bookmark the browser URL after customizing a variable font to revisit your last custom settings later, or select Copy URL to share or save your configuration.
Variable fonts in use
The customizable nature of variable fonts makes them perfect for a variety of applications, from digital graphics to product packaging or even vehicle wrapping. By adjusting the width, a font can be arranged so it is still readable on irregular surfaces.
Creative variable font settings can bring out a brand personality or accommodate long titles that often don’t fit in lower-third graphics.




Slant, weight, and width axes are used to adjust Obviously Variable to fit the car door panels. Acumin Variable is used for long lower-third titles.
You can use variable fonts to create a visual hierarchy on billboards and posters or tailor the variable font to tiny spaces and odd shapes in package design.




Variable fonts shine by creating better line breaking in paragraph justification. The width axis, in particular, allows for more efficient and visually pleasing word spacing.


Variable font capabilities allow them to perform well in responsive web design. One variable font can be used to adjust from small to large screen sizes, helping retain a small file size and decrease loading time.




Code snippets can be added to your CSS so that variable fonts animate, respond to sound, ambient light, or computer system theme. Variable font axes also make variable fonts easier to animate.


Type designers continue to explore new ways to interact and innovate with this font technology.