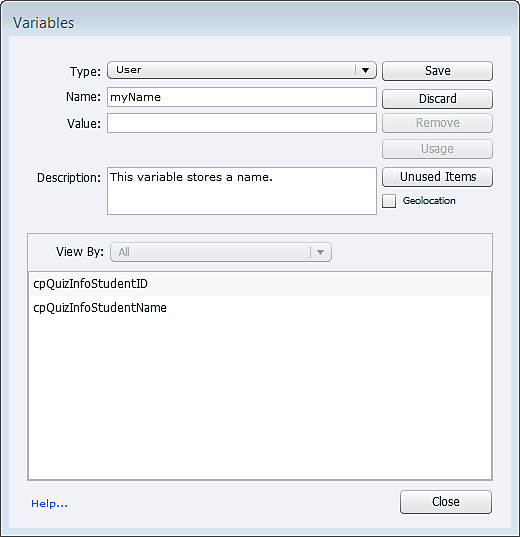
Click Project > Variables. The Variables dialog-box displays.
- Captivate Classic User Guide
- Introduction to Captivate
- Captivate Classic Release Notes
- Adobe Captivate Classic 11.8.4 Release Notes
- Adobe Captivate Classic 11.8.3 Release Notes
- Adobe Captivate Classic 11.8.2 Release Notes
- Adobe Captivate Classic 11.8.1 Release Notes
- Adobe Captivate Classic 11.8 Release Notes
- What's New in Adobe Captivate (2019 release) Update 5
- What's New in Adobe Captivate (2019 release) Update 2
- Adobe Captivate Release Notes
- Create Projects
- Create different types of projects in Adobe Captivate
- Customize the size of an Adobe Captivate project
- Responsive Project Design with Adobe Captivate
- Create Virtual Reality (VR) projects
- Work with responsive text in Adobe Captivate
- Work with themes in Adobe Captivate
- How to apply view specific properties in responsive projects
- How to create backup files for Adobe Captivate projects
- Asset panel
- Create branching and forced navigation in Captivate
- Replace image on the stage
- Add and Manage Objects
- Work with multi-state objects in Adobe Captivate
- Object effects
- Insert web objects in Adobe Captivate projects
- Work with object styles in Adobe Captivate
- How to rotate objects in Adobe Captivate
- How to manage objects with the Main Options toolbar
- How to merge objects in a slide
- How to manage objects in the library
- How to group objects in Adobe Captivate
- Edit object information using the Advanced Interaction panel
- How to copy, paste, and duplicate objects in Adobe Captivate
- Control the visibility of objects
- How to change the display order of objects in Adobe Captivate
- Apply shadows to objects
- How to align objects in Adobe Captivate
- How to add reflection to objects in Adobe Captivate
- Import assets into a Captivate project
- Slides
- Add slides to an Adobe Captivate project
- Editing slides in an Adobe Captivate project
- Delete Adobe Captivate project slides
- Change slide order in Adobe Captivate
- Set slide properties in Adobe Captivate
- Add and convert slide notes to audio files with Adobe Captivate
- Set up knowledge check slides in Adobe Captivate
- How to add slide transitions in Adobe Captivate
- How to work with master slides in Adobe Captivate
- How to lock Adobe Captivate slides
- How to hide or exclude slides in an Adobe Captivate project
- How to group and ungroup slides in Adobe Captivate
- Timeline and grids
- Create Quizzes
- Insert question slides in Adobe Captivate projects
- Set quiz preferences for Adobe Captivate
- How to enable learners to submit all quiz responses simultaneously
- How to set up question slides with Adobe Captivate
- Using random question slides in Adobe Captivate
- How to allow users to return to quiz
- Import questions from CSV format files
- Import questions from GIFT format files
- How to insert pretests in Adobe Captivate
- Audio
- Video
- Interactive Objects
- Interactions
- Non-interactive objects
- Create and edit smart shapes
- Edit and create text captions with Captivate
- How to use images and rollover images with Captivate
- How to customize smart shapes in Adobe Captivate
- How to create zoom areas in Adobe Captivate
- How to set audio for noninteractive objects
- How to create rollover slidelets in Adobe Captivate
- How to create rollover captions in Adobe Captivate
- Change mouse properties in Adobe Captivate
- Use highlight boxes in Captivate
- Work with swatches in Adobe Captivate
- Fix size and position of non-interactive objects
- Add animations to a Adobe Captivate project
- Advanced Editing and Project Reviews
- Variables and Advanced Actions
- Record Projects
- Publish Projects
- Preview and publish responsive projects
- Publish project to Adobe Captivate Prime
- Publish projects as HTML5 files with Adobe Captivate
- Publish projects as executable files
- Publish projects as MP4 files with Adobe Captivate
- Set publishing preferences in Adobe Captivate
- Using web fonts from Adobe Fonts in Adobe Captivate
- Report quiz results to an internal server
- Use Adobe Captivate with Other Applications
- Import and edit PowerPoint presentations in Captivate
- Upload an Adobe Captivate project to a Learning Management System
- Learn about the Common JavaScript interface for Adobe Captivate
- How to publish Captivate projects to Microsoft Word
- Using Adobe Connect with Captivate
- How to add Captivate projects to a RoboHelp online help system
- How to package multiple SCOs using the Adobe Multi-SCORM Packager
- Troubleshoot Adobe Captivate
- Resolve known issues and limitations in the latest versions of Adobe Captivate, Adobe FrameMaker, and Adobe RoboHelp.
- Early build for Captivate (2019 release) on macOS Big Sur (macOS 11)
- Hotfix for VR content not playing on devices
- Configure SSL for Live Preview on Devices
- Captivate (2019 release) activation issues on macOS Catalina
- Captivate responsive courses will not auto-play on browsers
- Issues with Asset panel in Adobe Captivate (2019 release)
- Error 103 while installing Adobe Captivate
- Issues when previewing a Captivate project
- Resolve known issues and limitations in the latest versions of Adobe Captivate, Adobe FrameMaker, and Adobe RoboHelp.
How to create user-defined variables in Adobe Captivate Classic
Like all programming languages, Captivate Classic uses variables to temporarily store values, which can be used by other components of Captivate Classic. In Captivate Classic, there are two types of variables, system and user-defined.
System variable: System variables come pre-defined with your copy of Captivate Classic. For example, cpCmndMute , which mutes the audio in a slide. For a list of all system variables, see Captivate Classic variables list.
User-defined variable: These are variables that you can create and assign them to customized actions. The name you assign to a user variable must not conflict with Captivate Classic’s internal functions, reserved keywords, exposed system variables, or other hidden variables.
There are some conventions while naming a variable. They are:
- Do not begin the name with a blank or a numeric character.
- Do not use any reserved keywords. The table below displays variable names that are reserved by ActionScript.
- Use unique variable names.
- Use intuitive names for a variable.
- Always add descriptions to a variable.
Creating a user-defined variable
In this example, we will create a user-defined variable and associate the variable with a button. When you click the button, a name displays.
To create the variable:
-
-
To add a variable, click Add New, and enter the variable information in the Name, Value, and Description fields.
- Name: Specify a unique name for the variable. Ensure that the name is intuitive enough to help users guess its content. For example, a variable storing the version number of a product would have the name ProductVersion or VersionNumber .
- Value: Specify a value for the variable. The value that you specify occurs at all instances of occurrence of the variable in the document. You can also choose to set the value later by leaving this field blank. Variables with undefined values appear as blank spaces in the project.
- Description: Optionally, add a description for the variable. For example, you could add a note for the authors instructing them about when to use the variable.
-
To save the changes, click Save.
-
In the Captivate Classic project, insert a button, a text entry box and a text caption, as shown below:
-
In the text entry box, you insert the variable you had created, as shown below:
-
With the cursor after the “:”, click [X] in the Property Inspector, as shown below:
Also, make the text caption hidden.
-
After you click Insert Variable or [X], in the Insert Variable dialog, click the Variables drop-down list, and choose the variable you created.
-
After you insert the variable, the variable name gets enclosed within $$...$$, as shown below:
Last ned
Some of the variable names are reserved by ActionScript. Do not use the following variable names when creating your variable:
alpha
currentframe
droptarget
focusrect
ramesloaded
height
buttonMode
byte
cacheAsBitmap
case
cast
catch
filters
final
finally
float
focusEnabled
focusRect
mouseX
mouseY
name
namespace
native
new
switch
synchronized
tabChildren
tabEnabled
tabIndex
textSnapshot
highquality
lockroot
name
parent
quality
rotation
char
class
const
constructor
contextMenu
continue
for
forceSmoothing
framesLoaded
function
get
goto
null
numChildren
opaqueBackground
override
package
parent
this
throw
throws
to
totalFrames
trackAsMenu
soundbuftime
target
totalframes
url
visible
width
currentFrame
currentLabel
currentLabels
currentScene
debugger
default
graphics
height
hitArea
if
implements
import
private
protected
prototype
public
return
root
transform
transient
true
try
type
typeof
x
xmouse
xscale
y
ymouse
yscale
delete
do
double
doubleClickEnabled
dropTarget
dynamic
in
include
instanceof
interface
internal
intrinsic
rotation
scale9Grid
scaleX
scaleY
scenes
scrollRect
use
useHandCursor
var
virtual
visible
void
abstract
accessibilityProperties
as
blendMode
boolean
break
each
else
enabled
enum
export
extends
false
is
loaderInfo
long
mask
menu
mouseChildren
mouseEnabled
set
short
soundTransform
stage
static
stop
super
volatile
while