In Adobe Bridge, choose Edit > Camera Raw Preferences (Windows) or Bridge > Camera Raw Preferences (macOS). Alternatively, click the Open Preferences Dialog button ![]() in the Camera Raw dialog box.
in the Camera Raw dialog box.
About camera raw files
A camera raw file contains unprocessed, uncompressed grayscale picture data from a digital camera’s image sensor, along with information about how the image was captured (metadata). Photoshop® Camera Raw software interprets the camera raw file, using information about the camera and the image’s metadata to construct and process a color image.
Think of a camera raw file as your photo negative. You can reprocess the file at any time, achieving the results that you want by making adjustments for white balance, tonal range, contrast, color saturation, and sharpening. When you adjust a camera raw image, the original camera raw data is preserved. Adjustments are stored as metadata in an accompanying sidecar file, in a database, or in the file itself (in the case of DNG format).
When you shoot JPEG files with your camera, the camera automatically processes the JPEG file to enhance and compress the image. You generally have little control over how this processing occurs. Shooting camera raw images with your camera gives you greater control than shooting JPEG images, because camera raw does not lock you into processing done by your camera. You can still edit JPEG and TIFF images in Camera Raw, but you will be editing pixels that were already processed by the camera. Camera raw files always contain the original, unprocessed pixels from the camera.
To shoot camera raw images, you must set your camera to save files in its own camera raw file format.
The Photoshop Raw format (.raw) is a file format for transferring images between applications and computer platforms. Don’t confuse Photoshop raw with camera raw file formats. File extensions for camera raw files vary depending on the camera manufacturer.
See the complete list of supported cameras here.
Digital cameras capture and store camera raw data with a linear tone response curve (gamma 1.0). Both film and the human eye have a nonlinear, logarithmic response to light (gamma greater than 2). An unprocessed camera raw image viewed as a grayscale image would seem very dark, because what appears twice as bright to the photosensor and computer seems less than twice as bright to the human eye.
To see a list of cameras and which version of Camera Raw each camera requires, see Cameras supported by Camera Raw.
About Adobe Camera Raw
Camera Raw software is included as a plug-in with Adobe After Effects® and Adobe Photoshop, and also adds functionality to Adobe Bridge. Camera Raw gives each of these applications the ability to import and work with camera raw files. You can also use Camera Raw to work with JPEG and TIFF files.
Camera Raw supports images up to 65,000 pixels long or wide and up to 512 megapixels. Camera Raw converts CMYK images to RGB upon opening.
You must have Photoshop or After Effects installed to open files in the Camera Raw dialog box from Adobe Bridge. However, if Photoshop or After Effects is not installed, you can still preview the images and see their metadata in Adobe Bridge. If another application is associated with the image file type, it’s possible to open the file in that application from Adobe Bridge.
Using Adobe Bridge, you can apply, copy, and clear image settings, and you can see previews and metadata for camera raw files without opening them in the Camera Raw dialog box. The preview in Adobe Bridge is a JPEG image generated using the current image settings; the preview is not the raw camera data itself, which would appear as a very dark grayscale image.
Note: A caution icon ![]() appears in the thumbnails and preview image in the Camera Raw dialog box while the preview is generated from the camera raw image.
appears in the thumbnails and preview image in the Camera Raw dialog box while the preview is generated from the camera raw image.
You can modify the default settings that Camera Raw uses for a particular model of camera. For each camera model, you can also modify the defaults for a particular ISO setting or a particular camera (by serial number). You can modify and save image settings as presets for use with other images.
When you use Camera Raw to make adjustments (including straightening and cropping) to a camera raw image, the image’s original camera raw data is preserved. The adjustments are stored in either the Camera Raw database, as metadata embedded in the image file, or in a sidecar XMP file (a metadata file that accompanies a camera raw file). For more information, see Specify where Camera Raw settings are stored.
After you process and edit a camera raw file using the Camera Raw plug-in, an icon ![]() appears in the image thumbnail in Adobe Bridge.
appears in the image thumbnail in Adobe Bridge.
If you open a camera raw file in Photoshop, you can save the image in other image formats, such as PSD, JPEG, Large Document Format (PSB), TIFF, Cineon, Photoshop Raw, PNG, or PBM. From the Camera Raw dialog box in Photoshop, you can save the processed files in Digital Negative (DNG), JPEG, TIFF, or Photoshop (PSD) formats. Although Adobe Camera Raw software can open and edit a camera raw image file, it cannot save an image in a camera raw format.
As new versions of Camera Raw become available, you can update this software by installing a new version of the plug-in. You can check for updates to Adobe software by choosing Help > Updates.
Different camera models save camera raw images in many different formats, and the data must be interpreted differently for these formats. Camera Raw includes support for many camera models, and it can interpret many camera raw formats.
If you have trouble opening Camera Raw files, see Why doesn't my version of Photoshop or Lightroom support my camera?
About the Digital Negative (DNG) format
The Digital Negative (DNG) format is a non-proprietary, publicly documented, and widely supported format for storing raw camera data. Hardware and software developers use DNG because it results in a flexible workflow for processing and archiving camera raw data. You may also use DNG as an intermediate format for storing images that were originally captured using a proprietary camera raw format.
Because DNG metadata is publicly documented, software readers such as Camera Raw do not need camera-specific knowledge to decode and process files created by a camera that supports DNG. If support for a proprietary format is discontinued, users may not be able to access images stored in that format, and the images may be lost forever. Because DNG is publicly documented, it is far more likely that raw images stored as DNG files will be readable by software in the distant future, making DNG a safer choice for archival storage.
Metadata for adjustments made to images stored as DNG files can be embedded in the DNG file itself instead of in a sidecar XMP file or in the Camera Raw database.
You can convert camera raw files to the DNG format by using the Adobe DNG Converter or the Camera Raw dialog box. For more information on the DNG format and DNG Converter, see the Digital Negative (DNG). You can download the latest version of Digital Negative (DNG) by selecting Windows or macOS.
Process images with Camera Raw
Copy camera raw files to your hard disk, organize them, and (optionally) convert them to DNG.
Before you do any work on the images that your camera raw files represent, transfer them from the camera’s memory card, organize them, give them useful names, and otherwise prepare them for use. Use the Get Photos From Camera command in Adobe Bridge to accomplish these tasks automatically.
Open the image files in Camera Raw.
You can open camera raw files in Camera Raw from Adobe Bridge, After Effects, or Photoshop. You can also open JPEG and TIFF files in Camera Raw from Adobe Bridge.
Adjust color.
Color adjustments include white balance, tone, and saturation. You can make most adjustments on the Basic tab, and then use controls on the other tabs to fine-tune the results. If you want Camera Raw to analyze your image and apply approximate tonal adjustments, click Auto on the Basic tab.
To apply the settings used for the previous image, or to apply the default settings for the camera model, camera, or ISO settings, choose the appropriate command from the Camera Raw Settings menu (see Apply saved Camera Raw settings).
Make other adjustments and image corrections.
Use other tools and controls in the Camera Raw dialog box to perform such tasks as sharpening the image, reducing noise, correcting for lens defects, and retouching.
(Optional) Save image settings as a preset or as default image settings.
To apply the same adjustments to other images later, save the settings as a preset. To save the adjustments as the defaults to be applied to all images from a specific camera model, a specific camera, or a specific ISO setting, save the image settings as the new Camera Raw defaults. (See Save, reset, and load Camera Raw settings.)
Set workflow options for Photoshop.
Set options to specify how images are saved from Camera Raw and how Photoshop should open them. You can access the Workflow Options settings by clicking the link beneath the image preview in the Camera Raw dialog box.
Save the image, or open it in Photoshop or After Effects.
When you finish adjusting the image in Camera Raw, you can apply the adjustments to the camera raw file, open the adjusted image in Photoshop or After Effects, save the adjusted image to another format, or cancel and discard adjustments. If you open the Camera Raw dialog box from After Effects, the Save Image and Done buttons are unavailable.
- Save Image Applies the Camera Raw settings to the images and saves copies of them in JPEG, PSD, TIFF, or DNG format. Press Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac OS) to suppress the Camera Raw Save Options dialog box and save the files using the last set of save options. (See Save a camera raw image in another format.)
- Open Image or OK Opens copies of the camera raw image files (with the Camera Raw settings applied) in Photoshop or After Effects. The original camera raw image file remains unaltered. Press Shift while clicking Open Image to open the raw file in Photoshop as a Smart Object. At any time, you can double-click the Smart Object layer that contains the raw file to adjust the Camera Raw settings.
- Done Closes the Camera Raw dialog box and stores file settings either in the camera raw database file, in the sidecar XMP file, or in the DNG file.
- Cancel Cancels the adjustments specified in the Camera Raw dialog box.
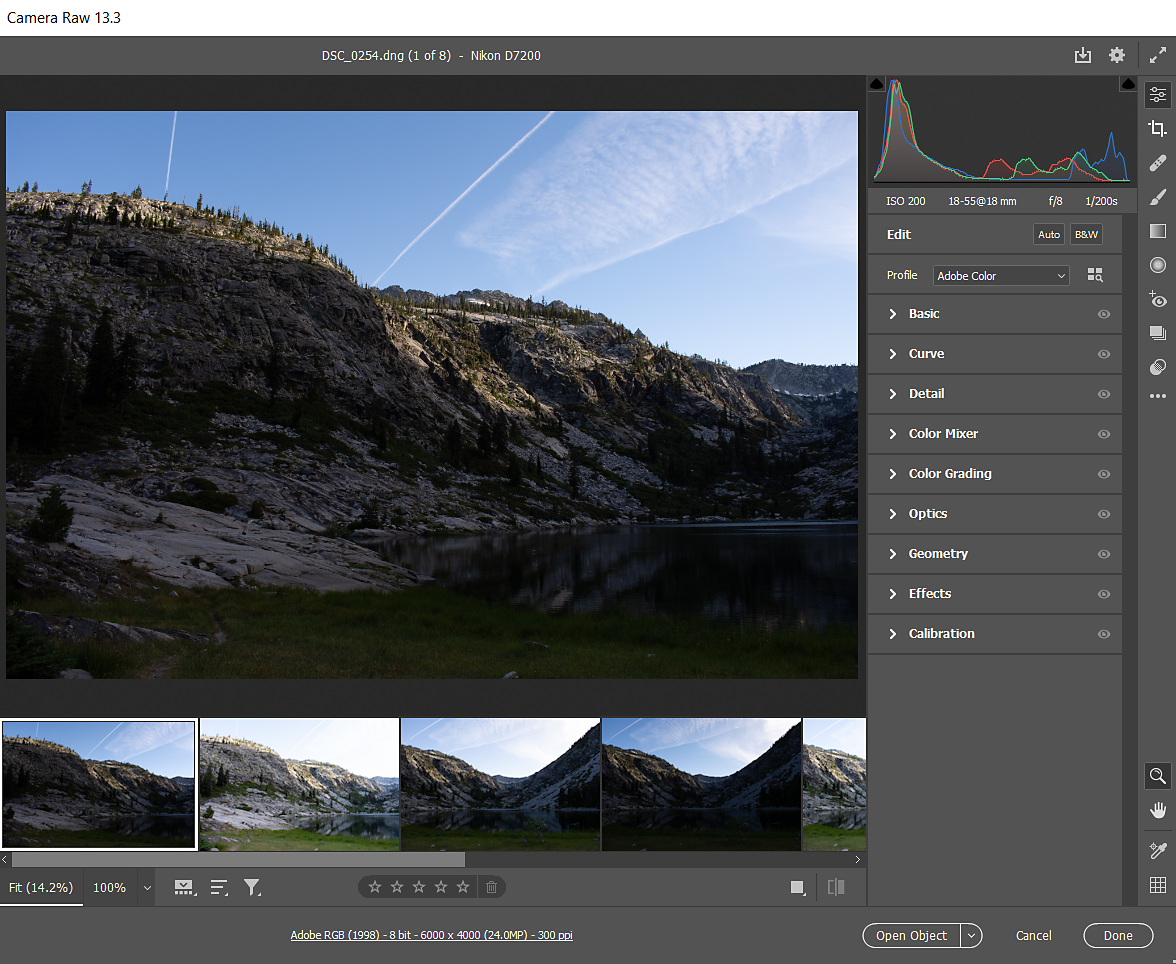



Use the Shadow and Highlight Clipping Indicators, on the upper-left and upper-right corner, respectively to view the areas of shadows and highlights in your image. Shadows are shown with a blue mask and highlights are shown in red.
Panels
Edit
Access Edit panels on the right side of the dialog box.
In Adobe Bridge, these options are also available from Edit > Develop Settings.
Open or collapse the panels as you need. Once you make adjustments in a panel, long-press the eye icon to hide that panel's adjustments in the preview. You can also select a profile from the Profile drop-down menu. Once you're made your desired adjustments, click Done.
Here are more details on the Edit panels:
- Basic Adjust White Balance, Temperature, Tint, Exposure, Highlight, Shadows, and more using the sliders
- Curve Fine-tune the tonal scale using curves. Select among Parametric Curve, Point Curve, Red Channel, Green channel, and Blue Channel
- Detail Adjust Sharpening, Noise Reduction, and Color Noise Reduction using the sliders
- Color Mixer Select between HSL (Hue, Saturation, Luminance) and Color to adjust different hues in your image
- Color Grading Precisely adjust hues in Shadows, Midtones, and Highlights using the color wheels. You can also adjust the Blending and Balance of these hues
- Optics Remove chromatic aberration or Distortion and Vignette. You can also use Defringe to sample purple or green hues in your image and correct them.
- Geometry Adjust different types of perspective and level corrections. Select Constrain crop to quickly remove the white border after applying Geometry adjustments
- Effects Add Grain or a vignette using the sliders
- Calibration Select the Process Version from the Process drop-down menu and adjust the sliders for Shadows, Red Primary, Green Primary, and Blue Primary
Crop and Rotate
Adjust Aspect Ratio and Angle. You can also rotate and flip your images.
Spot Removal
Heal or clone specific areas of your image.
Adjustment Brush
Make edits to specific areas of your image using the Brush tool.
Graduated Filter
Makes a selection using parallel lines. Adjust various controls based on the selected area.
Radial Filter
Makes a selection using an ellipse. Adjust various controls based on the selected areas.
Red Eye
Easily remove red eye or pet eye in images. Adjust Pupil Size or Darken.
Snapshot
Create and save different edited versions of your image.
Access and browse through Premium presets for Portraits for different skin tones, Cinematic, Travel, Vintage, and more. You can also find your User Presets here. Simply hover over a preset to preview and click to apply it.
Starting from Adobe Camera Raw version 14.4 (June 2022 release), you can control the intensity of the applied preset using the Preset Amount slider.


Preview
The selected image on the left displays a preview of the applied edits. You can cycle between the Before and After views by clicking the icon in the bottom-right corner. You can toggle between settings and parallely view an image with before and after edits. You can also temporarily hide edits from a panel when you long-press the eye icon of that panel.


Filmstrip
The images that you open in Camera Raw are displayed in the filmstrip, positioned below the preview. You can choose to hide the filmstrip, sort images based on Capture Date, File Name, Star Rating, and Color Label, and also filter photos using the Filter icon.
You can also move the filmstrip to the left panel, which is especially useful when working with portraits. To do this, Control-click (macOS)/Right-click (Windows) the filmstrip and select Filmstrip Orientation > Vertical.


Other controls
Zoom tool
Use the Zoom tool at the bottom of the right panel to zoom in or out of the preview image. Double-click the Zoom icon to return to Fit in View.
You can also control zoom using the Zoom level menu below the filmstrip. The default value is set to 100%.
Hand tool
When zoomed in, use the Hand tool to move around and view areas of the image in preview. Hold down the spacebar to temporarily activate the Hand tool while using another tool. Double-click the Hand tool to fit the preview image to the window.


Some controls such as the Workflow Options link, that are available when you open the Camera Raw dialog box from Adobe Bridge or Photoshop are not available when you open the Camera Raw dialog box from After Effects.
Learn how to use the Camera Raw filter in Adobe Photoshop
Work with the Camera Raw cache in Adobe Bridge
When you view camera raw files in Adobe Bridge, the thumbnails and previews use either the default settings or your adjusted settings. The Adobe Bridge cache stores data for the file thumbnails, metadata, and file information. Caching this data shortens the loading time when you return to a previously viewed folder in Adobe Bridge. The Camera Raw cache speeds the opening of images in Camera Raw and rebuilds of previews in Adobe Bridge when image settings change in Camera Raw.
Because caches can become very large, you may want to purge the Camera Raw cache or limit its size. You can also purge and regenerate the cache if you suspect that it is corrupted or old.
The Camera Raw cache holds data for about 200 images for each gigabyte of disk storage allocated to it. By default, the Camera Raw cache is set to a maximum size of 1 GB. You can increase its limit in the Camera Raw preferences.
-
-
Do any of the following:
- To change the cache size, enter a Maximum Size value.
- To purge the camera raw cache, click the Purge Cache button.
- To change the location of the camera raw cache, click Select Location.
Work with Camera Raw and Lightroom
Camera Raw and Lightroom share the same image-processing technology to ensure consistent and compatible results across applications. For Camera Raw to view image adjustments made in the Develop module of Lightroom, metadata changes must be saved to XMP in Lightroom.
Adjustments made in Camera Raw are also displayed in the Adobe Bridge Content and Preview panels.
To view Lightroom changes in Camera Raw, and to ensure that Camera Raw adjustments can be viewed in Lightroom and Adobe Bridge, do the following:
-
In Adobe Bridge, choose Edit > Camera Raw Preferences (Windows) or Bridge > Camera Raw Preferences (Mac OS). Or, with the Camera Raw dialog box open, click the Open Preferences Dialog button
 .
. -
Choose Save Image Settings In > Sidecar “.XMP” Files, and deselect Ignore Sidecar “.XMP” Files.
-
After applying adjustments to a photo in Camera Raw, save them by clicking Done or Open Image.
Camera Raw reads only the current settings for the primary image in the Lightroom catalog. Adjustments made to virtual copies are not displayed or available in Camera Raw.