Select the layer that you want to make partially transparent, and select Effect > Keying > Color Difference Key.
- After Effects User Guide
- Beta releases
- Getting started
- Workspaces
- Projects and compositions
- Importing footage
- Preparing and importing still images
- Importing from After Effects and Adobe Premiere Pro
- Importing and interpreting video and audio
- Preparing and importing 3D image files
- Importing and interpreting footage items
- Import SVG files
- Working with footage items
- Detect edit points using Scene Edit Detection
- XMP metadata
- Text and Graphics
- Text
- Motion Graphics
- Work with Motion Graphics templates in After Effects
- Use expressions to create drop-down lists in Motion Graphics templates
- Work with Essential Properties to create Motion Graphics templates
- Replace images and videos in Motion Graphics templates and Essential Properties
- Animate faster and easier using the Properties panel
- Variable Font Axes
- Drawing, Painting, and Paths
- Overview of shape layers, paths, and vector graphics
- Paint tools: Brush, Clone Stamp, and Eraser
- Taper shape strokes
- Shape attributes, paint operations, and path operations for shape layers
- Use Offset Paths shape effect to alter shapes
- Creating shapes
- Create masks
- Remove objects from your videos with the Content-Aware Fill panel
- Roto Brush and Refine Matte
- AI-powered Object Matte
- Create Nulls for Positional Properties and Paths
- Layers, Markers, and Camera
- Animation, Keyframes, Motion Tracking, and Keying
- Animation
- Keyframe
- Motion tracking
- Keying
- Transparency and Compositing
- Adjusting color
- Effects and Animation Presets
- Effects and animation presets overview
- Effect list
- Effect Manager
- Simulation effects
- Stylize effects
- Audio effects
- Distort effects
- Perspective effects
- Channel effects
- Generate effects
- Time effects
- Transition effects
- The Rolling Shutter Repair effect
- Blur and Sharpen effects
- 3D Channel effects
- Utility effects
- Matte effects
- Noise and Grain effects
- Detail-preserving Upscale effect
- Obsolete effects
- Cycore plugins
- Expressions and Automation
- Expressions
- Expression basics
- Understanding the expression language
- Using expression controls
- Syntax differences between the JavaScript and Legacy ExtendScript expression engines
- Editing expressions
- Expression errors
- Using the Expressions editor
- Use expressions to edit and access text properties
- Expression language reference
- Expression examples
- Automation
- Expressions
- Immersive video, VR, and 3D
- Construct VR environments in After Effects
- Apply immersive video effects
- Compositing tools for VR/360 videos
- Advanced 3D Renderer
- Import and add 3D models to your composition
- Import 3D models from Creative Cloud Libraries
- Create parametric meshes
- Image-Based Lighting
- Animated Environment Lights
- Enable lights to cast shadows
- Extract and animate lights and cameras from 3D models
- Tracking 3D camera movement
- Adjust Default Camera Settings for 3D compositions
- Cast and accept shadows
- Embedded 3D model animations
- Shadow Catcher
- 3D depth data extraction
- Enable in‑engine Depth of Field in Advanced 3D
- Modify materials properties of a 3D layer
- Apply Substance 3D materials
- Work in 3D Design Space
- 3D Transform Gizmos
- Single 3D Gizmo for multiple 3D layers
- Do more with 3D animation
- Preview changes to 3D designs real time with the Mercury 3D engine
- Stereoscopic 3D in After Effects
- Add responsive design to your graphics
- Views and Previews
- Rendering and Exporting
- Basics of rendering and exporting
- H.264 Encoding in After Effects
- Export an After Effects project as an Adobe Premiere Pro project
- Converting movies
- Multi-frame rendering
- Automated rendering and network rendering
- Rendering and exporting still images and still-image sequences
- Using the GoPro CineForm codec in After Effects
- Working with other applications
- Collaboration: Frame.io, and Team Projects
- Memory, storage, performance
- Knowledge Base
Though the color keying effects built into After Effects can be useful for some purposes, you should try keying with Keylight before attempting to use these built-in keying effects. Some keying effects have been superseded by more modern effects like Keylight.
The Color Difference Key effect creates transparency from opposite starting points by dividing an image into two mattes, Matte Partial A and Matte Partial B.
Matte Partial B bases the transparency on the specified key color, and Matte Partial A bases the transparency on areas of the image that don’t contain a second, different color. By combining the two mattes into a third matte, called the alpha ![]() matte, the Color Difference Key creates well-defined transparency values.
matte, the Color Difference Key creates well-defined transparency values.
The Color Difference Key produces high-quality keying for all well-lit footage items shot against a bluescreen or greenscreen and works especially well with images that contain transparent or semitransparent areas, such as smoke, shadows, or glass.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.








For information about keying in general, including links to tutorials and other resources, refer to Keying introduction and resources.
Use the Color Difference Key effect
-
-
In the Effect Controls panel, select Matte Corrected from the View menu.
To view and compare the source image, both partial mattes, and the final matte at the same time, select [A, B, Matte] Corrected, Final from the View menu.
Select the [A, B, Matte] Corrected, Final view to view the fully processed key as it will appear in your final composition. Select the [A, B, Matte] Corrected, Final view to view the fully processed key as it will appear in your final composition. Learn about other views available in the View menu.
-
Select the appropriate key color:
- To key out a bluescreen, use the default blue color.
- To key out a non-blue screen, select a key color in one of the following ways:
- Thumbnail eyedropper: Select and then use it in the Composition panel or the original thumbnail image on an appropriate area.
- Key Color eyedropper: Select and then use it in the Composition or Layer panel on an appropriate area.
- Key Color swatch: Select it and then a color from the specified color space.
NoteThe eyedropper tools move the sliders accordingly. Use the sliders to fine-tune the keying results.
-
Select the
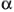 matte button to display the final combined matte in the matte thumbnail.
matte button to display the final combined matte in the matte thumbnail. -
Select the Black eyedropper, and then click inside the matte thumbnail on the lightest area of black to specify transparent regions. The transparency values in the thumbnail and Composition panel are adjusted.
-
Select the White eyedropper, and then click inside the matte thumbnail on the darkest area of white to specify opaque regions. The opaque values in the thumbnail and the Composition panel are adjusted.
NoteTo produce the best possible key, make the black and white areas as different as you can so that the image retains as many shades of gray as possible.
-
Select a matching accuracy from the Color Matching Accuracy menu. Select Faster unless you use a screen that isn’t a primary color (red, blue, or yellow). For those screens, select More Accurate, which increases rendering time but produces better results.
-
To further adjust transparency values, repeat steps 5 and 6 for one or both of the partial mattes. Select the Partial Matte B button or the Partial Matte A button to select a partial matte, and then repeat the steps.
-
Black sliders adjust the transparency levels of each matte. You can adjust the same levels using the Black eyedropper.
White sliders adjust the opaque levels of each matte. You can adjust the same levels using the White eyedropper.
Gamma sliders control how closely the transparency values follow a linear progression. At a value of 1 (the default), the progression is linear. Other values produce nonlinear progressions for particular adjustments or visual effects.
Adjust transparency for partial and final mattes using the matte controls sliders. Adjust transparency for partial and final mattes using the matte controls sliders. -
Before closing the Effect Controls panel, select Final Output from the View menu. Final Output must be selected for After Effects to render the transparency.
NoteTo remove traces of reflected key color from the image, apply Spill Suppressor using Better For Color Accuracy. If the image still has a lot of color, apply the Simple Choker or Matte Choker effect.
Color Key effect
The Color Key effect keys out all image pixels that are similar to a specified key color. This effect modifies only the alpha channel of a layer.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.
Key out a single color with the Color Key effect
-
Select the layer that you want to make partially transparent, and select Effect > Obsolete > Color Key.
-
In the Effect Controls panel, specify a key color in one of two ways:
Select the Key Color swatch to open the Key Color dialog box and specify a color.
Select the eyedropper, and then a color on the screen.
Specify a key color using the Key Color swatch or the eyedropper to select a color on the screen. Specify a key color using the Key Color swatch or the eyedropper to select a color on the screen. -
Drag the Color Tolerance slider to specify the range of color to key out. Lower values key out a smaller range of colors near the key color and higher values key out a wider range of color.
-
Drag the Edge Thin slider to adjust the width of the border of the keyed area. Positive values enlarge the mask, increasing the transparent area and negative values shrink the mask, decreasing the transparent area.
-
Drag the Edge Feather slider to specify the softness of the edge. Higher values create a softer edge but take longer to render.
Though the color keying effects built into After Effects can be useful for some purposes, you should try keying with Keylight before attempting to use these built-in keying effects. Some keying effects have been superseded by more modern effects like Keylight.
The Color Range effect creates transparency by keying out a specified range of colors in either the Lab, YUV, or RGB color space. You can use this key on screens that consist of more than one color or on bluescreens or greenscreens that have been unevenly lit and contain different shades of the same color.
This effect works with 8-bpc color.






Use the Color Range effect
-
Select the layer that you want to make partially transparent, and select Effect > Keying > Color Range.
-
Select Lab, YUV, or RGB from the Color Space menu. If you have trouble isolating the subject using one color space, try using a different one.
-
Use the Key Color eyedropper and then select in the matte thumbnail to choose the area that corresponds to a color in the Composition panel you want to make transparent. Typically, this first color is the one that covers the largest area of the image.
-
Select the plus eyedropper, and then click other areas in the matte thumbnail to add other colors or shades to the range of colors keyed out for transparency.
-
Select the minus eyedropper, and then click areas in the matte thumbnail to subtract other colors or shades from the range of colors keyed out.
-
Drag the Fuzziness slider to soften the edges between transparent and opaque regions.
-
Use the sliders in the Min and Max controls to fine-tune the color range you selected with the plus and minus eyedroppers.
The L, Y, R sliders control the first component of the specified color space, the a, U, G sliders control the second component, and the b, V, B sliders control the third component.
Drag the Min sliders to fine-tune the beginning of the color range and drag the Max sliders to fine-tune the end of the color range.
The Difference Matte effect creates transparency by comparing a source layer with a difference layer, and then keying out pixels in the source layer that match both the position and color in the difference layer. Typically, it’s used to key out a static background behind a moving object, which is then placed on a different background. Often the difference layer is simply a frame of background footage (before the moving object has entered the scene). For this reason, the Difference Matte effect is best used for scenes that have been shot with a stationary camera and an unmoving background.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.








Use the Difference Matte effect
-
Select a motion footage layer as the source layer.
-
In the source layer, find a frame that consists only of background, and save the background frame as an image file. Learn how to render and export a single frame of a composition.
-
Import the image file into After Effects, and add it to the composition.
The imported image becomes the difference layer. Make sure that its duration is at least as long as the duration of the source layer.
TipIf the shot doesn’t contain a full background frame, you may be able to assemble the full background by combining parts of several frames in After Effects or Photoshop. For example, you can use the Clone Stamp tool to take a sample of the background in one frame, and then paint the sample over part of the background in another frame.
-
Turn off the display of the difference layer by selecting the Video switch in the Timeline panel.
-
Make sure that the original source layer is selected, and then select Effect > Keying > Difference Matte.
-
In the Effect Controls panel, select Final Output or Matte Only from the View menu.
Use the Matte Only view to check for holes in the transparency. Learn more about filling undesired holes after you complete the keying process.
-
Select the background file from the Difference Layer menu.
-
If the difference layer isn’t the same size as the source layer, select one of the following controls from the If Layer Sizes Differ menu:
Center
Places the difference layer in the center of the source layer. If the difference layer is smaller than the source layer, the rest of the layer fills with black.
Stretch To Fit
Stretches or shrinks the difference layer to the size of the source layer. Background images may become distorted.
-
Adjust the Matching Tolerance slider to specify the amount of transparency based on how closely colors must match between the layers. Lower values produce less transparency and higher values produce more transparency.
-
Adjust the Matching Softness slider to soften the edges between transparent and opaque areas. Higher values make matched pixels more transparent but don’t increase the number of matching pixels.
-
If the matte still contains extraneous pixels, adjust the Blur Before Difference slider. This slider suppresses noise by slightly blurring both layers before the comparison is made.
NoteThe blurring occurs only for the comparison and doesn’t blur final output.
-
Before closing the Effect Controls panel, make sure to select Final Output from the View menu to ensure that After Effects renders the transparency.
The Extract effect creates transparency by keying out a specified brightness range, based on a histogram of a specified channel. It’s best used to create transparency in an image shot against a black or white background or against a background that is dark or bright but consists of more than one color.
The controls for this effect are similar to the controls of the Extract effect in Adobe Premiere Pro, but the purpose and results of the effect are different.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.
Use the Extract effect
In the Effect Controls panel, the Extract effect displays a histogram for a channel specified in the Channel menu. The histogram displays a representation of the brightness levels in the layer, showing the relative number of pixels at each level. From left to right, the histogram extends from the darkest (a value of 0) to the lightest (a value of 255).


Using the transparency control bar beneath the histogram, you can adjust the range of pixels that are made transparent. The position and shape of the bar in relation to the histogram determine transparency. Pixels corresponding to the area covered by the bar remain opaque; pixels corresponding to the areas not covered by the bar are made transparent.
-
Select the layer you want to make partially transparent, and select Effect > Keying > Extract.
-
If you are keying out bright or dark areas, select Luminance from the Channel menu. To create visual effects, select Red, Green, Blue, or Alpha.
-
Adjust the amount of transparency by dragging the transparency control bar in the following ways:
Drag the upper right or upper left selection handles to adjust the length of the bar and to shorten or lengthen the transparency range. You can also adjust the length by moving the White Point and Black Point sliders. Values above the white point and below the black point are made transparent.
Drag the lower right or lower left selection handles to taper the bar. Tapering the bar on the left affects the softness of transparency in the darker areas of the image; tapering it on the right affects the softness in the lighter areas. You can also adjust the softness levels by adjusting White Softness (lighter areas) and Black Softness (darker areas).
NoteTo taper the edges of the transparency control bar, first shorten the transparency bar.
- Drag the entire bar left or right to position it under the histogram.
Though the color keying effects built into After Effects can be useful for some purposes, you should try keying with Keylight before attempting to use these built-in keying effects. Some keying effects have been superseded by more modern effects like Keylight.
The Inner/Outer Key effect isolates a foreground object from its background.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.
Use the Inner/Outer Key effect
To use Inner/Outer Key, create a mask to define the inside and outside edges of the object you want to isolate. The mask can be fairly rough—it doesn’t need to fit exactly around the edges of the object.
In addition to masking a soft-edged object from its background, Inner/Outer Key modifies the colors around the border to remove contaminating background colors. This color decontamination process determines the contribution of the background to the color in each border pixel, and then removes that contribution—thus removing the halo that can appear if a soft-edged object is matted against a new background.
-
Select the border of the object that you want to extract by doing one of the following:
Draw a single closed mask near the border of the object; then select the mask from the Foreground menu and leave the Background menu set to None. Adjust the Single Mask Highlight Radius to control the size of the border around this mask. (This method works well only on objects with simple edges.)
Draw two closed masks– an inner mask just inside the object, and an outer mask just outside the object. Make sure that any fuzzy or uncertain areas of the object lie within these two masks. Select the inner mask from the Foreground menu and the outer mask from the Background menu.
NoteMake sure that the mask mode for all masks is set to None.
-
If you want, move the masks around to find the location that provides the best results.
-
To extract more than one object, or to create a hole in an object, draw additional masks and then select them from the Additional Foreground and Additional Background menus. For example, to key out a person’s hair blowing in the wind against a blue sky, draw the inner mask inside the head, draw the outer mask around the outside edge of the hair, and then draw an additional mask around the gap in the hair where you can see sky. Select the additional mask from the Additional Foreground menu to extract the gap and remove the background image.
-
Create additional open or closed masks to clean up other areas of the image, and then select them from the Cleanup Foreground or Cleanup Background menu. Cleanup Foreground masks increase the opacity along the mask; Cleanup Background masks decrease the opacity along the mask. Use the Brush Radius and Brush Pressure options to control the size and density of each stroke.
NoteYou can select the Background (outer) mask as a Cleanup Background mask to clean up noise from the background portions of the image.
-
Set Edge Thin to specify how much of the border of the matte is affected by the key. A positive value moves the edge away from the transparent region, increasing the transparent area; a negative value moves the edge toward the transparent region and increases the size of the foreground area.
-
Increase the Edge Feather values to soften edges of the keyed area. High Edge Feather values take longer to render.
-
Specify the Edge Threshold, which is a soft cutoff for removing low-opacity pixels that can cause unwanted noise in the image background.
-
Select Invert Extraction to reverse the foreground and background regions.
-
Set Blend With Original to specify the degree to which the resulting extracted image blends with the original image.
Linear keys create a range of transparency across an image. A linear key compares each pixel in the image to the key color you specify. If the color of a pixel closely matches the key color, it becomes completely transparent. Pixels that don’t match as well are made less transparent, and pixels that don’t match at all remain opaque. The range of transparency values, therefore, forms a linear progression.
The Linear Color Key effect uses RGB, hue, or chroma information to create transparency from a specified key color.
This effect works with 8-bpc, 16-bpc, and 32-bpc color.
Apply the Linear Color Key effect
In the Effect Controls panel, the Linear Color Key effect displays two thumbnail images; the left thumbnail image represents the unaltered source image, and the right thumbnail image represents the view you’ve selected in the View menu.
You can adjust the key color, the matching tolerance, and the matching softness. The matching tolerance specifies how closely pixels must match the key color before they start becoming transparent. The matching softness controls the softness of edges between the image and the key color.
You can also reapply this key to preserve a color that was made transparent by the first application of the key. For example, if you key out a medium-blue screen, you may lose some or all of a light-blue piece of clothing your subject is wearing. You can bring back the light-blue color by applying another instance of the Linear Color Key and selecting Keep Colors from the Key Operation menu.
-
Select a layer as the source layer, and then select Effect > Keying > Linear Color Key.
-
In the Effect Controls panel, select Key Colors from the Key Operation menu.
-
Select a color space from the Match Colors menu. In most cases, use the default RGB setting. If you have trouble isolating the subject using one color space, try using a different color space.
-
In the Effect Controls panel, select Final Output from the View menu. The view you choose appears in the right thumbnail and in the Composition panel. To see other results, work in one of the other views:
Source Only
Shows the original image without the key applied.
Matte Only
Shows the alpha channel matte. Use this view to check for holes in the transparency.
-
Select a key color in one of the following ways:
- Select the Thumbnail eyedropper, and then select an appropriate area in the Composition panel or the original thumbnail image.
- Select the Key Color eyedropper, and then select an appropriate area in the Composition or Layer panel.
- To preview transparency for different colors, select the Key Color eyedropper, hold down the Alt key (Windows) or Option key (macOS), and move the pointer to different areas in the Composition panel or the original thumbnail image. The transparency of the image in the Composition panel changes as you move the pointer over different colors or shades. Click to select the color.
- Select the Key Color swatch to select a color from the specified color space. The selected color becomes transparent.
NoteThe eyedropper tools move the sliders accordingly. Use the sliders in steps 6 and 7 to fine-tune the keying results. To use eyedroppers in the Layer panel, select Linear Color Key from the View menu in the Layer panel.
-
Adjust matching tolerance in one of the following ways:
- Select the Plus (+) or the Minus (-) eyedropper, and then click a color in the left thumbnail image. The Plus eyedropper adds the specified color to the key color range, increasing the matching tolerance and the level of transparency. The Minus eyedropper subtracts the specified color from the key color range, decreasing the matching tolerance and the level of transparency.
- Drag the matching tolerance slider. A value of 0 makes the entire image opaque; a value of 100 makes the entire image transparent.
-
Drag the Matching Softness slider to soften the matching tolerance by tapering the tolerance value. Typically, values under 20% produce the best results.
-
Before closing the Effect Controls panel, make sure to select Final Output from the View menu to ensure that After Effects renders the transparency.
Preserve a color after applying Linear Color Key
-
In the Effect Controls panel or Timeline panel, turn off any current instances of keys or matte effects by deselecting the Effect option to the left of the key name or tool name. Deselecting the option causes the original image to appear in the Composition panel so that you can select a color to preserve.
-
Choose Effect > Keying > Linear Color Key. A second set of Linear Color Key controls appears in the Effect Controls panel below the first set.
-
In the Effect Controls panel, choose Keep Colors from the Key Operation menu.
-
Select the color you want to keep.
-
In the first application of the Linear Color Key effect, choose Final Output from the View menu in the Effect Controls panel, and then turn other instances of the Linear Color Key effect back on to examine the transparency. You may need to adjust colors or reapply the key a third time to get the results you need.
Luma Key effect
The Luma Key effect keys out all the regions of a layer with a specified luminance or brightness. The quality setting of the layer doesn’t influence the Luma Key effect.
Use this effect if the object from which you want to create a matte has a greatly different luminance value than its background. For example, if you want to create a matte for musical notes on a white background, you can key out the brighter values; the dark musical notes become the only opaque areas.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.






Key out a luminance value with the Luma Key effect
-
Select the layer that you want to make partially transparent, and select Effect > Obsolete > Luma Key.
-
Select a Key Type to specify the range to be keyed out.
-
Drag the Threshold slider in the Effect Controls panel to set the luminance value you want the matte to be based on.
-
Drag the Tolerance slider to specify the range of values to be keyed out. Lower values key out a smaller range of values near the threshold, while higher values key out a wider range of values.
-
Drag the Edge Thin slider to adjust the width of the border of the keyed area. Positive values make the mask grow, increasing the transparent area, while negative values shrink it.
-
Drag the Edge Feather slider to specify the softness of the edge. Higher values create a softer edge but take longer to render.
The Unmult effect keys out all the regions of a layer with a solid black or white background, making those areas transparent.
Use this effect if you need to remove a solid black or white background from footage while preserving the colors and details of the foreground for compositing or other visual effects. For example, you can use this effect to isolate an object shot against a black or white background, such as paint splashes, smoke, or other elements, and integrate them seamlessly into a different scene.
This effect works with 8-bpc, 16-bpc, and 32-bpc color.




Apply the Unmult effect
-
Select the layer from which you want to remove black or white backgrounds to isolate the subject, then go to Effect > Keying > Unmult.
-
The effect removes colors based on their brightness levels relative to the selected background color, so use the Background Color dropdown menu and select from the following options:
- If the background is black, you adjust the black level to remove darker areas while keeping the subject intact.
- If the background is white, you adjust the white level to remove brighter areas.
-
If you select the Background color as Black, use the Black Level slider in the Effect Controls panel to work with dark areas.
Moving the slider handle to the left lowers the threshold, keeping more dark areas opaque. Moving it to the right raises the threshold, making more dark areas transparent.
Use the Black Level slider in the Effect Controls panel to work with the dark areas of the selected layer. Use the Black Level slider in the Effect Controls panel to work with the dark areas of the selected layer. -
If you select the Background color as White, use the White Level slider in the Effect Controls panel to work with the brighter areas.
Moving the slider handle to the left lowers the threshold, removing colors that are brighter than the set value, while moving the slider to the right raises the threshold, keeping more of the brighter areas opaque.
Use the White Level slider in the Effect Controls panel to work with the brighter areas of the selected layer. Use the White Level slider in the Effect Controls panel to work with the brighter areas of the selected layer. -
Use the Softness slider to control the transition between transparent and opaque areas, creating a smoother gradient rather than a hard cutoff.
When the softness is set to 0, the transition is sharp, and as you increase the softness, it creates a gradual falloff.
-
Select and enable the Remove Color Matting feature to restore the original, unblended colors of an image or footage by removing the influence of the background color from semi-transparent areas.
It works by identifying the background color (e.g., white) and proportionally removing it from semi-transparent areas. It then restores the colors to what they likely were before blending with the background. For example, if red paint was blended against a white background, this feature tries to remove the white influence and restore the original red color.
-
Select and enable Clip HDR Results to limit color values in HDR footage to avoid extreme or unexpected results when working with negative values or values above 1 during the Remove Color Matting process.
Spill Suppressor effect
Starting with the June 2014 release of After Effects CC, the Spill Suppressor effect has been moved to the Obsolete effects category and users are recommended to use the Advanced Spill Suppressor effect.
Key Cleaner and Advanced Spill Suppressor effect
The Key Cleaner effect recovers alpha-channel detail from a scene keyed by a typical keying effect, including recovering detail lost due to compression artifacts.
If you see that unwanted semi-transparency effects have crept in along edges that should be sharp, use an effect mask (with a little mask feather) to restrict the Key Cleaner effect to the intended area.
The Advanced Spill Suppressor effect removes color spill on a foreground subject from a colored background used for color keying.
The Advanced Spill Suppressor effect has two methods for spill suppression:
- Standard - The Standard method is simpler, automatically detects the dominant key color, and requires less user input.
- Ultra - The Ultra method is based on the spill suppression in the Ultra Key effect in Premiere Pro. Learn more about Ultra Key in the Ultra Key section of Premiere Pro.
An easy way of applying these effects is by using the Keylight + Key Cleaner + Spill Suppressor animation preset.
Starting with the June 2014 release of After Effects CC, the Spill Suppressor effect has been moved to the Obsolete effects category and users are recommended to use the Advanced Spill Suppressor effect.
After Effects includes several built-in keying effects, as well as the Academy Award–winning Keylight effect, which excels at professional-quality color keying.
- For information on the Keylight effect, refer to the documentation in the folder in which the Keylight plug-in is installed.
- For information about keying in general, including links to tutorials and other resources, refer to Keying introduction and resources.
The Key Color property is already linked with an expression to the Keylight effect's Screen Colour property, so you don't need to change it unless you want to use a different color for the despill process. To use a different color for the despill process, just disable or remove the Keylight expression.
Using the Keylight + Key Cleaner + Advanced Spill Suppressor animation preset
Follow the steps below to apply the Keylight effect with the Key Cleaner and Advanced Spill Suppressor effect:
- Use the Keylight + Key Cleaner + Advanced Spill Suppressor animation preset to apply the three effects in order to the layer. The Advanced Spill Suppressor effect is turned off by default to allow you to sample the key color in the Keylight effect, or if the footage does not have any color spill to be removed.
- Use the Keylight effect's Screen Colour eyedropper to sample the key color from the layer in the Composition panel. Adjust other Keylight effect settings as you normally would to get the best results.
- Turn on the effect switch for the Advanced Spill Suppressor effect to remove color spill from the scene, if required.
If you see unwanted semitransparency along edges that should be sharp, use an effect mask (with a little bit of mask feather) to restrict Key Cleaner to the intended area.
Learn about variable-width mask feathering and soften the edges of a mask.
Using Key Cleaner and Advanced Spill Suppressor effects with other keying effects
Follow the steps below to apply the Key Cleaner and Advanced Spill Suppressor effect to a keying effect other than the Keylight effect:
- Apply the keying effect to the layer.
- Set the effect to the equivalent of the Keylight effect's Indeterminate Result setting, so that the keying effect gives the full RGB result without attempting to perform its own spill suppression.
- Apply the Key Cleaner effect after the keying effect.
- Apply the Advanced Spill Suppressor effect after the Key Cleaner effect.
Learn Tutorial
Watch this video to learn how to get better keying results from compressed or badly shot green-screen footage with the new Key Cleaner effect and remove color spill with the Advanced Spill Suppressor controls.


![In the Effect Controls panel, the Color Difference Key effect's controls are open. The view dropdown menu is open and the [A, B, Matte] Corrected, Final is selected from the View menu](https://helpx-prod.scene7.com/is/image/HelpxProd/keying-effects-04-ae?$pjpeg$&jpegSize=200&wid=1200)



